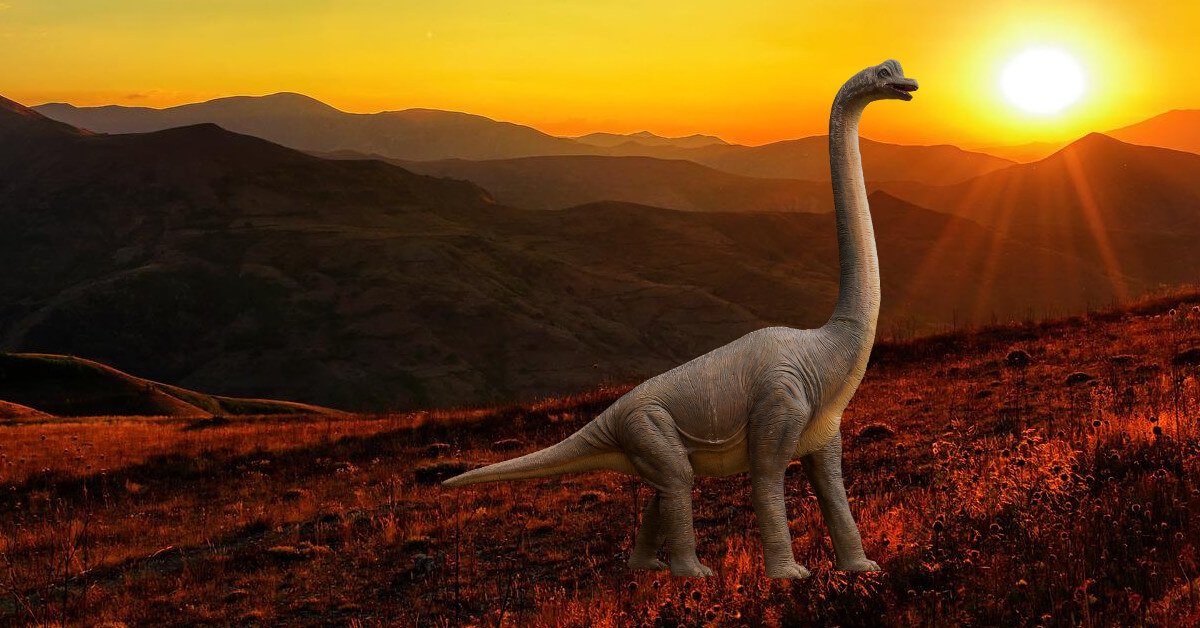
The Brontosaurus is back! Brontosaurus is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that was first discovered in 1878 and from 1903 until 2015, it was considered the same dinosaur as the Apatosaurus, but in 2015 the Brontosaurus was reclassified as a separate genus. It is, however, closely related to the Apatosaurus. Both are sauropods (a group of herbivore dinosaurs with a very long neck, long tails, four legs, and a small head).

Brontosaurs had long necks and tails; these are thought to be adaptations that allowed them to reach leaves high up in trees, presumably while on the ground or wading through water. This dinosaur was 22 meters (72 feet) long, about the same as a city bus, and weighed up to 15 tonnes – as much as 3 African elephants (the heaviest living land mammal). They weren’t as fast as a bus, though! With a body of that size and weight, they are thought to reach speeds of about 10 miles per hour (16 kilometers per hour).
This dinosaur should not be confused with the similarly named Apatosaurus (which means “deceptive lizard”) or Diplodocus (“double beam”).
They lived around 157,3 – 145 million years ago during the Late Jurassic period in North America.
Brontosaurus means "Thunder Lizard"
By studying fossil evidence, scientists believe they know quite a bit about how Brontosaurus looked and behaved.
Brontosaurus is renowned for its notable size, and its tall, slender build led to the nickname “thunder lizard.”
As with many other dinosaur discoveries in the late 19th century, Brontosaurus became a household name after being featured in books like Sir Arthur Conan Doyle’s The Lost World. Today it is the official state dinosaur of Colorado.
They swallowed stones that helped them to digest food.
Brontosaurs were herbivores, meaning they only ate plants. It’s thought that these animals swallowed stones, which allowed them to grind up the plant material in their stomachs. In addition, they had tiny molars in their front jaw; they likely picked up food from bushes and trees while still standing on the ground by using their long necks and then swallowed it whole without chewing much.
Brontosaurus is a heavy dinosaur!
It’s likely that these giant creatures eat more than 600 kg (more than 1320 lbs!) and spend 80% of their day eating plants.
Brontosaurs lived in herds. Young brontosaurs were most likely kept close to their mothers by solid family bonds, while the rest of the herd was organized into groups led by an older female.
The fossil record suggests that they lived in herds for protection against predators and allowed them to migrate safely between feeding grounds. They may have used signals including body posture (head high or tail swinging), vocalizations, and possibly even scents to communicate with each other. Brontosaurs may have been so big that they were not bothered by most predators. Their heavy bodies may have also helped them to escape predators by charging head-first into trees and undergrowth.
While adult brontosaurs were safe, their young may have been at risk of being attacked by dinosaurs like Allosaurus.
The Brontosaurs lived alongside many other sauropods in North America during the Late Jurassic, including Apatosaurus, Camarasaurus, Diplodocus, and Barosaurus.
In a nutshell:
- Brontosaurus is a type of sauropod (a group of dinosaurs with a long neck, long tail, four legs, and herbivores)
- Brontosaurus comes from Greek and means “thunder lizard.”
- It was up to 22 meters (72 feet) long and 15 tons heavy
- It was one of the first dinosaurs to be discovered in 1878. In 1903 it was classified as the same species as the Apatosaurus, but in 2015 it was reclassified as a different genus.
- It’s closely related to the Apatosaurus, but there are some distinctions.
- They lived around 157,3 – 145 million years ago during the Late Jurassic period in what is now North America.